5G Technology: History, Concept, Features and Constraints:
Historical Background
History of Wireless Cellular
Technology
Way
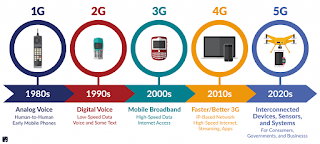
back in the 1950s, the first commercial analog mobile communication system was
launched in the US. It had very low market penetration for years after its
launch. Formally speaking, the first generation (1G) mobile phone was
launched three decades later and continued to use analog signals. With the
advent of microprocessors and the dawn of the digital age, analog mobile
communication was digitized and we had a second generation of mobile
communication (2G) technology enter the picture. 2G was fully digital,
i.e., dealing only with 1s and 0s. Besides improving the quality of voice
transmission and reception, 2G also introduced SMS—a feature that
millennials used with devotedly before instant messengers like WhatsApp
arose and changed the social lives of “netizens”.
A couple of years later, General Packet Radio Services (GPRS) was added to
2G, which allowed users to browse the internet on mobile
devices. Although the speed compared to present-day broadband/4G was
extremely slow (even in general, cable internet speed was slow), GPRS gave
consumers the first taste of Internet access on mobile devices. At the turn of
the new millennium, third-generation (3G) tech came into existence,
thus allowing users to access the Internet at a decent speed in addition
to providing the standard telephone features of voice calls and messaging.
Just a few years back, 4G was launched, meaning that internet
communication could now happen at a super-fast rate
(100Mbps, theoretically) on 4G-enabled devices. Internet penetration in the
industrial/commercial segment is much deeper with sensor-based smart
devices/appliances being used almost everywhere. Thus, there is a need for
technology that has enough bandwidth to cater to the rising number of
devices and provide uninterrupted high-speed Internet so that the
waiting/processing time is negligible. Such devices include a smartphone utilizing the Internet, television, fridge other wearable
electronics, and even a car. This is what 5G is designed for.
Introduction
What is 5G?
We
understand the motivation behind the need for 5G, but what exactly is it?
Well, 5G is the advanced newest (fifth) generation of mobile cellular
technology and is intended to vastly improve the Internet speed, coverage, and
latency of wireless networks. Speed is usually the most discerning factor
between the changing generations of wireless cellular technology. So how fast
is 5G, you ask?
Well, it’s
tough to give you a precise number, as 5G infrastructure is still
a work-in-progress with standards that have yet to be finalized.
However, you can roughly assume 5G to be around 10 to 100 times faster than
your present-day cellular connection. In fact, it’s even faster than anything
you can get with a physical fiber-optic cable. To get a better understanding,
think of downloading a 4K movie in a matter of seconds. Yeah, that may seem
incredible, but you would probably be able to accomplish that with a 5G system
in place.
Mission
With
any type of 5G connection, you'll see faster network speeds. Currently, the
fastest 4G mobile networks offer around 45Mbps (megabits per second) speeds,
although the industry is still hopeful of achieving the sought after 1Gbps
(gigabit per second = 1,000Mbps). According to chipmaker Qualcomm, 5G
could achieve browsing and download speeds about 10 to 20 times
faster than current 4G technologies. Early adopters of 5G technology might
not notice vastly higher speeds at first. The true speed you get will on early
5G networks will depend heavily on both the spectrum band the operator chooses
to run their 5G technology and on and how much your carrier has invested in
new masts and transmitters.
Vision
The
global deployment of LTE cultivates the mobile users to be used to the mobile
data in their daily life tremendously. The video service and social
applications, for example, WeChat, Facebook, and Twitter have changed our life
very much with the capabilities of LTE, especially high data rate and low
latency. It is believed that mobile communication will penetrate into every
element of future society and create an all-dimensional, user-centered
information ecosystem. A fully mobile and connected society is expected in the
near future, which will be characterized by a tremendous amount of growth in
connectivity, traffic volume, and a much broader range of usage scenarios.
Accordingly, the Mobile Broadband (MBB) service and the Internet of Things
(IoT) will be the two main drivers in the future development of mobile
communications, and they will provide a broad prospect for the next generation
mobile communication system (5G), the overall vision of which is depicted.
Mobile Broadband service disrupted the traditional business model of mobile
communications, enabling unprecedented user experiences and making a profound
impact on every aspect of people’s work and life. Looking ahead to the year
2020 and beyond, there will be explosive growth in mobile data traffic. It is
estimated that the global mobile data traffic will grow by more than 200 times
from 2010 to 2020 and by nearly 20,000 times from 2010 to 2030. In China, the
growth factors are projected to be even higher, with mobile data traffic being
expected to grow by more than 300 times from 2010 to 2020 and by more than
40,000 times from 2010 to 2030. For developed cities and hotspots in China, the
growth of mobile data traffic will exceed the projected average growth for all
of China. For example, from 2010 to 2020 in Shanghai, mobile data traffic
is projected to grow by 600 times. In Beijing and during this same period, it
is estimated that hotspot traffic may grow by up to 1,000 times. The IoT has
extended the scope of mobile communications services from interpersonal
communications to the smart interconnection between things and between people and
things, allowing mobile communications technologies to penetrate into broader
industries and fields. Looking ahead to the year 2020 and beyond, applications such
as mobile health, Internet of Vehicles (IoV), smart home, industrial control,
and environmental monitoring will drive the explosive growth of IoT
applications, facilitating hundreds of billions of devices to connect to a
network creating a true
Values
Here’s
a list of top 5 valuable facts about 5G technology:
1.
It helps in the development of better business communication
2.
It has better signal communication across the globe
3.
It is more important in IoT technology, taking things to get connected to the internet
such as a car, fridge, and other electronics.
4.
It helps in the deployment of virtual reality and augmented reality
technologies
5.
It has a wide range of fast communication.
Problems
1.
Deployment and coverage
Despite 5G offering a significant increase in
speed and bandwidth, its more limited range will require further
infrastructure. Higher frequencies enable highly directional radio waves,
meaning they can be targeted or aimed at — a practice called beamforming. The
challenge is that 5G antennas while being able to handle more users
and data, beam out over shorter distances.
2.
Cost to build, cost to buy
Building
a network is expensive, and carriers will raise the money to do it by increasing
customer revenue. Much like LTE plans incurred a higher initial cost, 5G will
probably follow a similar path. And it’s not just building a layer on top of an
existing network — it’s laying the groundwork for something new altogether. According
to Heavy Reading’s Mobile Operator 5G Capex, total global spending on 5G
is set to reach $88 billion by 2023. Once it becomes truly viable, certain
device segments will be connected in entirely new ways, particularly vehicles,
appliances, robots, and city infrastructure.
3. The Radio Frequency May Become a
Problem
Radios,
cell towers and even satellites communicate using radio frequencies. Frequency
is measured in Hz and the radio frequencies tend to operate in the GHz range.
Early reports on the 5G network indicate that this network is going to
transmit its data in the range of around 6 GHz. Unfortunately, this radio
frequency range is already crowded by other signals, such as satellite links.
With numerous types of signals operating in the range of 6 GHz, it is fair to
wonder whether or not the overcrowding is going to pose a problem as people try
to transmit their data signals at this frequency. Will there be issues sending
and receiving signals? Time will tell as this network frequency starts to
spread.
4. Health Problems – What We Know
About Electromagnetic Frequency (EMF)
The
rise of 5G technology will usher in even more wireless devices, not only
cellphones and tablets but smart appliances and autonomous vehicles as well.
Having 5G means the wireless network can accommodate more users without the
speeds slowing down. This also means users are more exposed to harmful
electromagnetic frequency (EMF) radiation that is emitted by these gadgets, not
to mention, the 5G towers themselves. The NTP study, according to the American
Cancer Society marked “a paradigm shift in our understanding of radiation and
cancer risk.” It might have reopened the debate on the potentially harmful
effects of cellphone radiation on people’s health.
Wireless-safety
advocates reiterated that there is a need for more research before Americans
can start using 5G as there are serious concerns about consumer health safety.
For now, they are pushing for the use of protective products such as cases and
headsets that will limit the gadget user’s exposure to radio-frequency
radiation.
Challenges/Constraints
Challenges are the inherent part of the new development; so, like
all technologies, 5G has also big challenges to deal with. As we see past i.e.
development of radio technology, we find very fast growth. Starting from 1G to
5G, the journey is mere of about 40 years old (Considering 1G in 1980s and 5G
in the 2020s). However, in this journey, the common challenges that we observed are
lack of infrastructure, research methodology, and cost.
Technological Challenges
·
Inter-cell
Interference − This is one of the major
technological issues that need to be solved. There are variations in the size of
traditional macrocells and concurrent small cells that will lead to
interference.
·
Efficient
Medium Access Control − in a situation, where dense
deployment of access points and user terminals are required, the user
throughput will be low, latency will be high, and hotspots will not be
competent in cellular technology to provide high throughput. It needs to be
researched properly to optimize technology.
·
Traffic
Management − in comparison to the traditional human to
human traffic in cellular networks, a great number of Machine to Machine (M2M)
devices in a cell may cause serious system challenges i.e. radio access network
(RAN) challenges, which will cause overload and congestion.
Common Challenges
·
Multiple
Services − unlike other radio signal services, 5G would
have a huge task to offer services to heterogeneous networks, technologies, and
devices operating in different geographic regions. So, the challenge is of
standardization to provide dynamic, universal, user-centric, and data-rich
wireless services to fulfill the high expectation of people.
·
Infrastructure −
Researchers are facing technological challenges of standardization and
application of 5G services.
·
Communication,
Navigation, & Sensing − these services largely
depend upon the availability of radio spectrum, through which signals are
transmitted. Though 5G technology has a strong computational power to process a huge volume of data coming from different and distinct sources, it needs
larger infrastructure support.
·
Security
and Privacy − this is one of the most
important challenges that 5G needs to ensure the protection of personal data. 5G
will have to define the uncertainties related to security threats including
trust, privacy, cyber-security, which are growing across the globe.
·
Legislation
of Cyberlaw − Cybercrime and other fraud may
also, increase with the high speed and ubiquitous 5G technology. Therefore,
legislation of the Cyberlaw is also an imperative issue, which largely is
governmental and political (national as well as an international issue) in nature.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
1.
5G is more speedy than the previous generation
2.
It has a wide range of features such as future technologies
Weaknesses
1.
Mobile phones of today are 4G-based devices, 5G-supported devices are very costly
2.
It is very costly to use or build
Opportunities
1.
International corporations have huge opportunities in the fast delivery of products
2.
5G technology has no competitor now
Threats
1.
It has a high radiation frequency, it is dangerous to human lives
2.
It has cybersecurity challenges
Features
5G technology going to be a new mobile revolution in the mobile
market. Through 5G technology now you can use worldwide cellular phones and
this technology also strikes the china mobile market and a user being proficient
to get access to Germany phone as a local phone. 5G technology has
extraordinary data capabilities and has the ability to tie together unrestricted
call volumes and infinite data broadcast within the latest mobile operating system.
5G technology has a bright future because it can handle the best technologies and
offer priceless handsets to its customers. Maybe in the coming days, 5G technology
takes over the world market. 5G Technologies have an extraordinary capability
to support Software and Consultancy. The Router and switch technology used in
5G network providing high connectivity. The 5G technology distributes internet
access to nodes within the building and can be deployed with the union of wired or
wireless network connections. The current trend of 5G technology has a glowing
future.
5G technology offer a high resolution for crazy cell phone
user and bi-directional large bandwidth shaping.
·
The
advanced billing interfaces of 5G technology makes it more attractive and
effective.
·
5G
technology also providing subscriber supervision tools for fast action.
·
The
high-quality services of 5G technology based on Policy to avoid an error.
· 5G
technology is providing large broadcasting of data in Gigabit which supporting
almost 65,000 connections.
·
5G
technology offers transporter class gateway with unparalleled consistency.
·
The
traffic statistics by 5G technology makes it more accurate.
·
Through
remote management offered by 5G technology a user can get better and fast
solution.
·
The
remote diagnostics also a great feature of 5G technology.
·
The
5G technology is providing up to 25 Mbps connectivity speed.
·
The
5G technology also support virtual private network.
·
The
new 5G technology will take all delivery service out of a business prospect
·
The
uploading and downloading speed of 5G technology touching the peak.
·
The
5G technology network offering enhanced and available connectivity just about
the world
Benefits
Below
are some benefits of 5G technology:
- Improved
network capacity and throughput with peak data speeds up to 20 Gbps
downlinks and up to 10 Gbps uplinks
- Network
management of up to 1 M devices per square kilometer, improved device
mobility of up to 500 kilometers per hour, over 100x energy efficiency
over 4G LTE, and one millisecond network latency times allowing use cases
such as cellular V2X and public safety communications
- 5G
development is leading to new services and uses cases for wireless
customers
- Spectrum
support for many frequencies, including spectrum bands above 6 GHz,
availability of TDD and FDD modes for all bands, and use of licensed and
unlicensed bands
·
The fifth-generation wireless systems,
known as 5G, could be up to 100 times faster than 4G and will power the
“Internet of Things,” including telemedicine and autonomous vehicles.
Impacts
CB
Insights identified the 20 industries that 5G will impact the most. Here are
the top 10:
1.
Manufacturing
5G
is poised to help manufacturing production operations become more flexible and
efficient, while also improving safety and lowering maintenance costs.
2.
Energy and utilities
Critical
infrastructure like energy and utilities will benefit from 5G technologies,
which could create more innovative solutions in energy production,
transmission, distribution, and usage, as well as the next wave of smart grid
features and efficiency.
3.
Agriculture
Farmers
worldwide are using IoT technology to optimize agricultural processes
including water management, fertigation, livestock safety, and crop monitoring,
the report noted. 5G could enable real-time data collection, allowing farmers
to monitor, track, and automate agricultural systems to increase profitability,
efficiency, and safety.
4.
Retail
More
than 100 million Americans made a purchase on their smartphone in 2018, the report noted, and the move to mobile shopping is largely due to the rise of
4G/LTE. The faster speeds 5G will bring will enable new retail experiences like
virtual reality (VR) dressing rooms.
5.
Financial services
5G
will accelerate the digitization of financial institutions, including from
internal operations to customer service, the report said. Increased security
and speed will allow users to increasingly make transactions instantly on their
devices, and make remote tellers a possibility.
6.
Media and entertainment
5G
will bring about new opportunities in mobile media, mobile advertising, home
broadband, and TV, as well as interactive technologies like VR and augmented
reality (AR).
7.
Healthcare
In
the healthcare industry, 5G could increase efficiencies and revenue, helping
health systems create faster, more efficient networks to keep up with the large
amounts of data involved. The technology could also enable the use of remote
monitoring devices to improve health outcomes.
8.
Transportation
Transportation
systems ranging from public buses to private logistic fleets will gain
increased visibility and control thanks to 5G, the report said. 5G will allow
improved vehicle-to-vehicle communications, enabling more self-driving car
testing. These networks will also help cities gain access to more data around
their transportation systems.
9.
AR/VR
The
future of AR and VR depends on reliable 5G networks, according to the report.
These technologies require a less expensive, wider network with lower latency
to continue developing and reaching widespread adoption, as they require
massive amounts of data processing.
10.
Insurance
5G
will help insurance agents make more effective decisions, as they will have
access to more accurate data, the report said.
Recommendations
The nation that leads in developing and widely deploying 5G technology will have an
important first-mover advantage, with both economic and national security
implications. Chinese national champion Huawei is the current global
leader in 5G, and China’s ZTE is also a major player in the industry. Huawei is
aggressively pursuing export of its 5G systems to install digital
infrastructure around the globe. Huawei is an attractive option to many nations
because it is cheaper than its competitors. The products of firms competing
with Chinese companies will be more expensive because of unfair subsidies from
the Chinese Communist Party, which artificially reduce prices.
Huawei
is a tool of state power and a critical asset in China’s global economic and
geopolitical competitions and ambitions. Huawei faces competition from Samsung
USA and others as an end-to-end producer, and still other companies produce 5G
components (such as antennae, chips, and base station architecture) including
Ericsson, Nokia, and Qualcomm. These firms are more expensive because they are
not the beneficiaries of unfair state subsidies. However, they offer other
advantages, including enhanced security, more rigorous training of personnel,
protection of intellectual property, and privacy. 5G should be recommended as:
·
A national campaign should be launched to inform the public about
5G and its critical importance to the economy and national security.
·
The administration needs to accelerate plans for the whole-of-government process to develop a long-term national spectrum strategy
and the creation of an ongoing inter-spectrum (mid-band) for 5G that allows the US to synchronize federal, state, and local policies and procedures to
facilitate the rapid and cost-efficient deployment of 5G network equipment.
Conclusion
In
conclusion, we’ve learned that 5G technology is not mere fiction; it has
existed. We’ve learned that much about it such as its benefits, challenges,
problems, threats, and we will conclude that 5G technology is an advanced
technology that no civilized country would want to dump. It has a wide range
of features, it supports our future technologies such as IoT, AR/VR, and many
others. So, 5G technology is an essential advanced technology the world would
need and be fully developed worldwide in this New Year, 2020, the year of 5G
network development.
References
[1] Science ABC, “What Is 5G Technology? How
Will It Change The Way You Use The Internet?”, https://www....com
[2] TutorialsPoint.com, “5G – Challenges”, https://www.tutorialspoint.com/5g/5g_challenges.htm
[3] RPC Senate, “The Importance of 5G”, https://www.rpc.senate.gov/policy-papers/the-importance-of-5g
[4] FreeWimaxInfo.com, “What is 5G Technology
and Features”, http://freewimaxinfo.com/5g-technology.html
[5] Futurithmic.com, “Five of the biggest
challenges facing 5G”, https://www.futurithmic.com/category/thetechnology/
[6] WhatsAg.com, “The Advantages and
Disadvantages of a 5G Network”, https://whatsag.com/5g/5g_advantages_and_disadvantages.php
[7] Vesttech.com, “Does 5G Internet Cause More
Health Problems?”, https://www.vesttech.com/can-5g-internet-cause-more-health-problems/
[8] G. Liu and D. Jiang (2016), “5G: Vision and
Requirements for Mobile Communication System towards Year 2020”
[9] CB Insights, “5G will impact these 10
industries the most”, https://www.cbinsights.com/research/5g-technology-disrupting-industries
[10] Atlantic Council, “Recommendations on 5G and
National Security”, https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/issue/security-defense/
Note: This research work has been carried out by Muhammad Auwal Ahmad AKA Mohiddeen Ahmad, the founder of Flowdiary.



Comments